User Tools
Site Tools
Table of Contents
Mesh Network
General
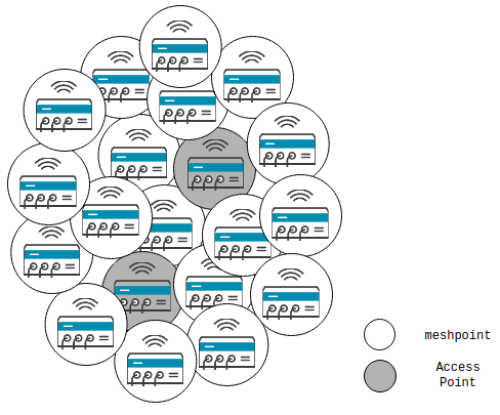
A mesh network (WMN), also called IEEE 802.11s or meshed network, connect different devices within a network structure. Mesh describes a network topology (structure) in which each network node is connected to another and data is constantly exchanged with each other. The topology of the mesh network can easily be transferred to a wireless (WiFi) network.
A wifi mesh network consists of several access points (AP) and meshpoints that continuously communicate with each other and at the same time with the integrated network devices. Usually routers in the 2.4 and 5 GHZ frequency range. The new mesh devices also use a third radio module, with which they mesh together. As a result, the signals are not attenuated, but passed on in full. Unlike repeaters, the mesh units not only reinforce an existing WLAN network, but also generate the same WLAN signal themselves.
Advantages
- LAN Bridging
- Reliability
- Easy expandability
- Self-healing
- Great coverage
Disadvantages
- High effort & costs to build up mesh network topology
- High energy consumption to guarantee permanent functionality
Configuartion
Netmodule devices support mesh functionality since software version 4.2.0.100
The wiki was tested with router software 4.8.0.105
Network Setup
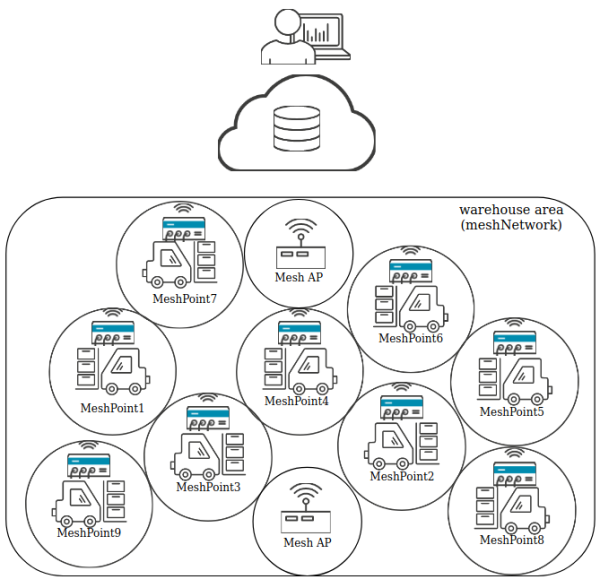
The following schematic and configuration guideline show a typically use case of mesh technologie. The diagram shows a warehouse with several heavy-load stacker vehicales. The warehouse area has a regulated traffic conception, which makes it easier to arrange and define the mesh network area. All vehicales are equiped with Netmodule Router Netmodule Router units and acting as meshpoint, interact with each other and form the mesh network. As enddevice all stackers are also equiped with scanners to capture the loaded goods. As soon as any data has been generated, the mesh functionality will automatically find the shortest path through the network to the endpoint(cloud). [This use case is fictitious, but might be a regualar use case.]
Meshpoint
1. Define operation mode
- Choose “mesh point” as prefer operation Mode
- Choose prefered 2.4GHz chanel (in this example Chanel 6)
2. Define MESH ID
- Choose a name as MESH ID. (in this example “WLAN-SPS”)
- Choose prefered security mode and define a passphrase (SAE security mode recommended)
3. Define IP settings
- Choose “DHCP Client” as prefer setting
All other meshpoints which want to be integrated into the mesh-network need to be configured in the same way“
Mesh Gateway
A mesh gateway is typically the transition point to another network or the way to the internet. In this example we going to modify a Netmodule meshpoint into a mesh gateway. The unit also contents an addtional mobile interface for internet connection. All generated traffic out of the mesh network will be routed into the internet.
1. Define operation Mode
- Choose “mesh point” as prefer operation Mode
- Choose prefered 2.4GHz chanel (in this example Chanel 6)
2. Define MESH ID
- Choose a name as MESH ID. (in this example “WLAN-SPS”)
- Choose prefered security mode and define a passphrase (SAE security mode recommended)
- enable “gate announcements”
3. Define IP settings
- Choose “DHCP Client” as prefer setting
3. Define bridge interface
- Choose “LAN1” as bridging interface to use DHCP Server out of LAN1 for the mesh IP network.
Limitations NB800/1601
- Maximum number of connected peers per single peer in the network 10
- Maximum number of nodes in the entire network 32
- Maximum number of hops in network 6