Table of Contents
Voice support
The NetModule Router Series NB2000 and NB3000 support voice and audio communication with two extension:
- Voice-License (“V”) GSM-Voice to VoIP/SIP to make or receive PSTN voice call over the mobile network.
- Audio (“A”) stereo line-in/out to VoIP/SIP to connect audio signals directly to the device. Typical microphone and loudspeaker via external amplifier.
- Push-to-Talk (“Ap”) mono line in/out to connect audio signals directly to the device, 1/1 digital in/out e.g. for call & ring signaling
Basic concept
An endpoint is a SIP/VoIP device like
- Internal GSM-Voice
- Internal Audio-Interface
- External SIP-Phone, PBX, door station etc.
To establish a call two steps are needed:
- Signalling = establish a call
- Call-Routing = making the connection
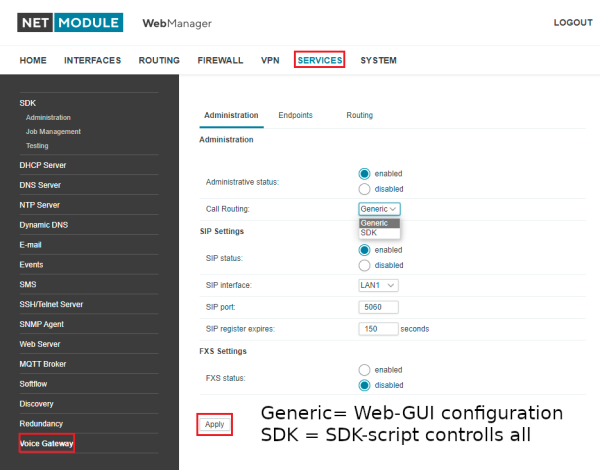
Simple behaviour can be configured by the Web-GUI. For more complex applications the SDK can be used.
Voice gateway configuration via Web GUI
Using the router with a SIP phone client.
Administration
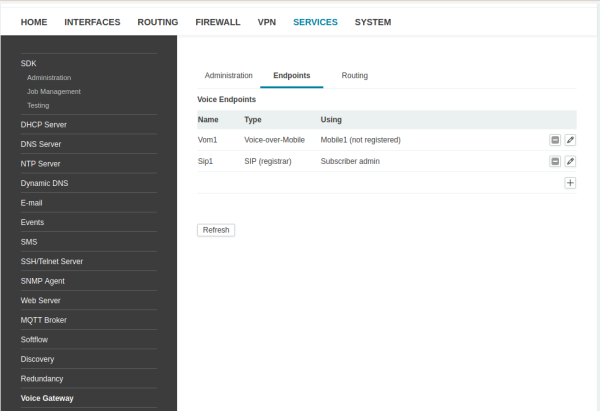
Endpoints
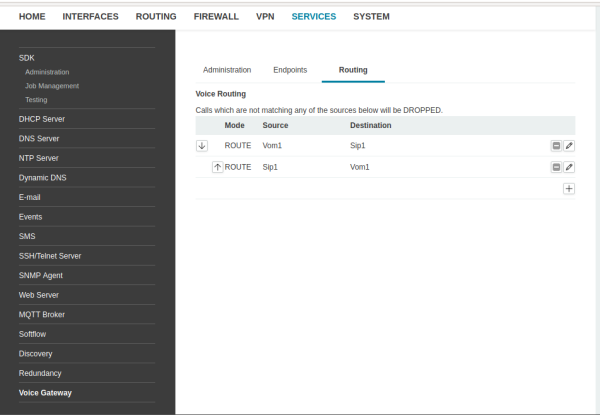
Routing
Routing modes
SDK scripts
Endpoints are represented as structs
struct(3): {
.id = int: 54321
.desc = string[5]: "vom://Vom1"
.state = string[4]: "busy"
.volume = = int: 7
};
Descriptors
- Sip1 First SIP subscriber
- Vom1 First Voice-Over-Mobile
- Aud1 First Audio device
- sip:⁄⁄user@192 .168.1.254:5060 SIP address
States
- busy endpoint is already holding a call
- available endpoint is ready to take a call
Calls are represented as structures which may look like:
struct(5): {
.id = int: 12345
.state = string[7]: "dialing"
.calling = string[24]: "sip://user@192 .168.1.254:5060"
.called = string[22]: "vom://+123456789 @Vom1"
};
The following states are possible:
- routing call is in routing state
- dialing call is in dialing state
- alerting call is in alerting state
- active call is active
- hungup call had hung up
Voice functions:
- array nb_voice_endpoint_list (void) / struct nb_voice_endpoint_get (endpoint)
- Unordered List Itemarray nb_voice_call_list (void) / struct nb_voice_call_get (call)
- int nb_voice_call_dial (call)
- int nb_voice_call_accept (call)
- int nb_voice_call_route (call, endpoint)
- int nb_voice_call_hangup (call)
- int nb_voice_call_volume (endpoint, int level)
How to make a call
Start Call
- Unordered List Itemnb_voice_call_dial(call) or wait for call
Event magement
- Unordered List ItemOutgoing – do nothing
- Incomming - nb_voice_call_route(call, target endpoint)
- Dispatched: alerting → nb_voice_call_accept(call)